CornerNet: Detecting Objects as Paired Keypoints : https://arxiv.org/abs/1808.01244
CornerNet: Detecting Objects as Paired Keypoints
We propose CornerNet, a new approach to object detection where we detect an object bounding box as a pair of keypoints, the top-left corner and the bottom-right corner, using a single convolution neural network. By detecting objects as paired keypoints, we
arxiv.org
CenterNet: Keypoint Triplets for Object Detection : https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.08189
CenterNet: Keypoint Triplets for Object Detection
In object detection, keypoint-based approaches often suffer a large number of incorrect object bounding boxes, arguably due to the lack of an additional look into the cropped regions. This paper presents an efficient solution which explores the visual patt
arxiv.org
CornerNet
Abstract
object detection의 새로운 접근법으로, Pair of keypoint를 통해 Object bounding box를 탐지한다.
2개의 keypoint : top-left corner, bottom-right corner
method : a single convolution neural network
이전 single-stage detectors에서 사용된 anchor boxes를 설계할 필요가 없어졌다.
corner pooling는 코너를 찾는데 활용할 수 있게 새롭게 도입된 pooling layer
Intro
Anchor Box : One-stage detector가 경쟁력과 효율성을 얻기 위해 사용된 방법
Anchor 예측 방법 : One-stage detector는 anchor box들의 점수를 매기고, 회귀로 좌표를 정제하여 최종 박스 위치 예측
Anchor의 단점 :
- need a very large set of anchor box(DSSD에서는 40K가 필요)
- Ground Truth의 작은 부분으로 huge imbalance를 야기시킴
- need many hyperparameters and design choice
- 갯수, 크기, 비율 등
- multiple resolution인 경우, 별개의 예측을 진행(using different features and each anchor size)
CornerNet : Anchor box가 없는 object detection의 a new one-stage approach
pair of keypoints -> 1) top-left corner(tlc), 2)bottom-right corner(brc)
CornerNet의 구성
single convolutional network :
- 같은 object category의 모든 instance에 대한 tlc, brc의 히트맵(heat map)을 예측
- 각 corner의 임베딩(embedding) 벡터 예측
- embedding : 같은 오브젝트에 속하는 코너의 짝을 그룹핑하기 위해
- Train 목적 : network는 같은 오브젝트의 tlc와 brc가 비슷한 임베딩을 예측하도록 훈련받는다.
corner pooling : a new type of pooling layer
- 역할 : localize corners
- 문제 : 기존 코너들은 대부분 오브젝트의 외부를 가리키므로 지역 정보로는 얻을 수 없다.
- Sol : 픽셀 위치를 결정하기 위해 수직, 수평상의 값을 비교하는 방식
- 계산 : tlc를 결정하기 위해 2개의 Feature map을 사용하여 각각 수직, 수평 방향으로
maxpooling을 진행하여 서로 더하게 한다.
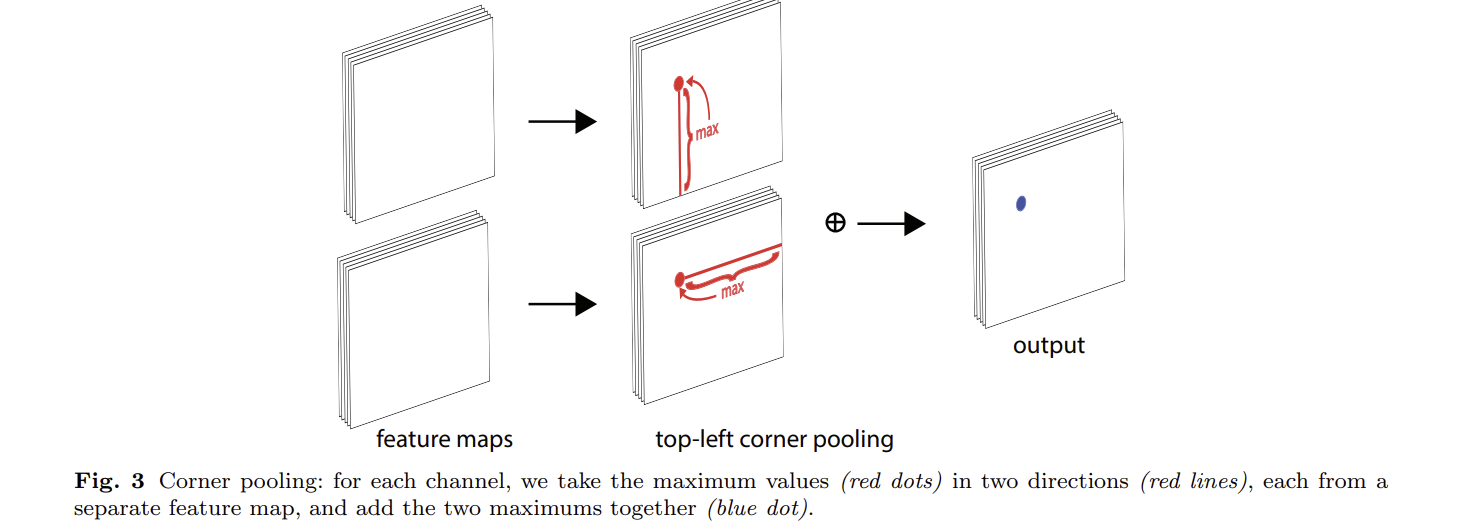
장점 : 적은 코너 개수 : O(wh) < O(w^2h^2)
Related Works
DeNet은 RoI를 anchor box 없이 생성함.
처음에는 각 위치가 top-left인지 bottom-right에 속하는지 결정
다음에는 모든 코너 조합을 열거함으로써 RoI들을 생성한다.
이후 2단계 접근을 통해 RoI를 분류
DeNet과의 차이점
1. DeNet은 2개의 코너가 같은 오브젝트로부터라면 확인하지 않고,
Poor RoI의 거부는 sub-detection network에 의존한다.
우리 방식
1.One-stage approach
- detect + groups the corner (using single ConvNet)
2. DeNet : 분류를 위한 상대적인 지역에 미리 결정된 위치에서 특징을 선택
Our : X need feature
selection step
3. Our : corner pooling :
for corner detection
Our inspired by Newell
1. detect + group을
single network로 이 접근으로 detected는 embedding vector로
2. 우리만의 방식은 cornerpooling
> for localizing the corners
3. modify the hourglass architecture
4. add novel variant of
focal loss _ train network
3. CornerNet
3.1 overview
- heatmap : 다른 오브제의 코너들의 위치를 표현하기 위해 구함
- embedding vector : 같은 오브제의 코너간의 vector 거리는 가깝다
- offset : 코너의 위치를 조정하기 위해 사용
구성
backbone : hourglass network _ feature 출력
prediction module : tlc, brc을 예측, (+ corner pooling module)
- corner pooling module : pool features from the hourglass network
Process
backbone -> 2개의 prediction module -> output(heatmap, embedding and offset)

3.2 Detecting Corners
predict two sets of heatmap : tlc, brc
set of heatmap : C channel (C = number of categories), size : H*W
- channel : 클래스의 코너들의 위치를 가리키는 Binary mask
Penalizing the negative location : positive location로 부터 일정 radius 내의 negative location인 경우 패널티를 줄이도록 함.
radius 크기 결정 : radius는 object의 크기에 따라 결정됨( 일정 크기 이상의 IoU를 보장하도록)
패널티를 줄이는 방식 : penalty reduction은 2D 가우시안 분포를 생성하여 감소시킴

x,y는 positive location의 위치, 시그마는 radius의 1/3

각 클래스별 코너 위치를 확률 히트맵으로 예측하고, 그 히트맵 학습하기 위한 loss 함수
pcij : 예측된 히트맵에서 class c에 대한 location(i,j)의 점수
ycij : ground-truth heatmap _ 가우시안으로 증강
N : number of object
알파, 베타 : hyperparameter
(1-y) : reduce the penalty
네트워크의 Downsampling layer를 전역정보(global information)를 얻거나 메모리 사용을 줄이기 위해 사용한다.
이 과정에서 heatmap에서 image로 remap시, 정보 손실이 나오므로 remapping 전에 offset을 활용하여 위치를 조정한다.
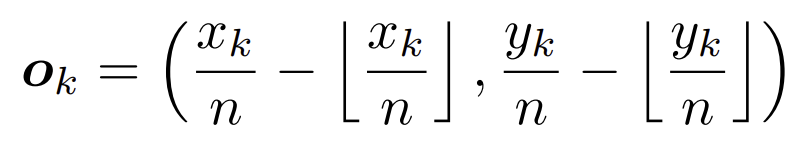
xk, yk는 corner k의 좌표


3.3 Grouping Corners
한 이미지에 여러 오브제가 있는 경우에는 여러 코너가 나온다.
embedding하는 방법은 'Associative Embedding: End-to-End Learning for Joint Detection and Grouping' 에서 제안한 방법
목적 : 같은 bounding box의 corner인지를 결정하기
network가 탐지된 코너를 통해 embedding vector를 예측
벡터 간의 거리 기반으로 그룹핑 진행


etk : k 오브제의 top-left corner의 embedding
ebk : k 오브제의 bottom-right corner의 embedding
Lpull : group
Lpush : separate the corners
3.4 Corner Pooling
corner pooling은 max pooling 방식으로 진행함
top-left의 경우 수직방향으로 수평방향으로 각각 maxpooling을 진행한 2개의 feature map을 같이 더해준다

top-left : (i,j) -> (i,H) and (W,j)
bottom-right : (0,j), (i,0) -> (i,j)

3.5 Hourglass Network
Hourglass Network
: Fully convolutional neural network
( 1개 이상의 hourgalss 모듈로 구성됨)
1st : downsamples the input feature
- convolution과 max pooling layer를 통해
2nd : upsamples
feature back to the original resolution
- upsampling과 convolution layer를 통해
max pooling : lost the detail
skip layer : bring details to the upsampled features by added
hourglass module은 global+local feature를 단일의 unified structure에서 가져온다.
여러 hourglass module이 쌓인 네트워크인 경우, hourgalss module들은 feature를 재처리하여 높은 단계의 정보 생성
Hourglass network는 2개의 hourglass로 구성
- modification : maxpooling -> stride 2 _ to reduce the feature resolution
- 5번 진행
- feature channel는 256, 384, 384, 384, 512로 변화함
Upsample에서 2개의 residual module을 적용하고, 가까운 이웃 업샘플링을 적용
모든 skip connection에서는 2개의 residual module로 구성됨
512 channel로 된 4 residual module이 hourglass module의 중앙에 있다.
hourglass moduel 전의 작업
이미지 해상도 줄이기 : 4배 줄이기
- ( 7*7 convolution module + stride 2, 128 channels)
- 이후에 residual block( stride 2, 256 channels)
훈련에서 중간 감독을 추가함.
X 중간의 예측을 네트워크에 넣지 않음
우리는 3*3 Conv-BN module을 HM(hourglass module)의 입력, 출력에 적용함.
이후 요소별로 덧셈, ReLU와 256 channel의 residual block을 병합함
- 이는 2번째 HM의 input으로 사용
depth : 104
마지막 층의 feature만을 사용해서 예측을 구함'
모델 성능

CenterNet : Keypoint Triplets for Object Detection
keypoint 기반의 접근법은 부정확한 bounding box를 만듦
이는 cropped region에 대한 추가적인 조사가 없기에 발생함
이 논문에서는 cropped 지역의 시각적 패턴을 적은 비용으로 조사한다.
이 프레임워크는 CornerNet에 기반하여 작성되었고, 여기서 pair of points가 아닌 triplet로 탐지한다.
설계된 모델 : cascade corner pooling and center pooling
- 수집된 정보를 풍부하게 하는 역할
- 중심 지역에 더욱 인식 가능한 정보를 제공
1. Intro
Object Detection : 1)Anchor, 2)Key-point
Anchor : manually designed, ground-truth box에 정렬되지 않기에 분류 작업에 도움이 안 됨
Keypoint : ConrnerNet, Anchor의 우회와 One-stage object detection에서 성과를 이룸
문제) 전역 정보를 참조하는 능력이 부족함
- Pair of keypoints를 통해 경계를 찾는 능력은 좋았지만, 어느 object에 속해야 하는 지 모름
Sol : CornerNet + Perceiving the visual patterns within proposed region 를 통해 각 bbox를 식별할 수 있게 한다.
CenterNet : 중심 부분을 조사하는 저예산+효과적인 모델
가정 : high IoU > cental keypoint가 중심 지역의 클래스와 같을 거라고 예측하는 확률이 높을 것이다.
proposal에 2개의 keypoint를 생성 후 keypoint의 중심을 검사하여 같은 클래스의 여부를 검사( triplet )
제안 : keypoint 탐지를 향상하기 위해서 2갸지 방법 제안
1) Center pooling : center keypoint에 인식 가능한 시각적 패턴을 얻도록 도움
얻는 방법 : center keypoint들을 예측하기 위한 feature map에서 center keypoint의
수평, 수직 방향들의 max summed response으로 얻음
2) Cascade corner pooling : 내부 정보를 인지할 수 있는 corner pooling module
얻는 방법 : corner를 예측하기 위한 feature map의 오브젝트의 경계쪽, 내부쪽 방향들의
max summed response
위의 2가지 방향의 풀링 방식은 더욱 안정되었기에, precision 과 recall의 향상을 기여했다.
2. Related Work
Two-stage approaches divide the object detection task into two stages: extract RoIs, then classify and regress the RoIs.
One-stage approaches remove the RoI extraction process and directly classify and regress the candidate anchor boxes.
3. Our Approach
3.1 Baseline and Motivation
- CornerNet을 Baseline으로 사용
CornerNet's process
- Produce two heatmap of top-left corners and bottom-right corners
- Assign a confidence score for each keypoint
- Predict embedding and a group of offset
bbox 생성시
- select top-k left-top, bottom-right corners from the heatmaps
- calculate the distance of the embedding vectors of a pair of corner
- if the distance is less than threshold, 경계박스에 신뢰점수 할당

해석 : FD5 = 32.7
32.7% FD rate at IoU = 0.05
100개의 bbox에서 32.7개가 IoU보다 낮게 나왔음을 보여준다.
이에 대한 원인으로 CornerNet이 bbox의 내부 지역을 조사할 수 없다는 점으로 생각했습니다.
이를 위한 해결안으로 CornerNet에 RoI pooling을 추가한 two-stage detector도 생각했지만 비용문제가 발생
CenterNet : 시각적 패턴 조사, pair이 아닌 triplet을 이용, one-stage detector이며 부분적으로 RoI pooling을 상속함
2개의 pooling을 사용하여 visual pattern을 keypoint detection process에 추가로 도입했다.
3.2 Object Detection as Keypoint Triplets

히트맵, 임베딩과 오프셋구하기
위의 프레임워크에서는 각 오브제의 center keypoint와 pair를 가져오고,
center keypoint는 CornerNet에 기반하여 히트맵을 임베딩하고, 오프셋 예측
예측 값을 이용해 선별하는 과정
1. 점수에 따라 top-k keypoint 선별
2. 오프셋을 사용하여 중심 키포인트를 입력 이미지에 다시 매핑한다.
3. 각 bbox의 중심 지역(central region)을 정의하고, 중심 지역에 center keypoint를 포함하는지 검사
*검사된 center keypoint의 class label은 bbox와 같아야 함
4. 중심 지역에 center keypoint가 있는 경우 bbox의 점수를 3 point의 평균 점수로 대체
아닌 경우 그 bbox는 제거
central region의 크기
big size : low precision
small size : low recall
Sol : The scale-aware central region
The scale-aware central region
- bbox보다 상대적으로 큰 central region과 상대적으로 작은 central region을 생성
- i bbox를 정의하고, 해당 좌표 ( tl_x, tl_y, br_x, br_y ) 정의
- central region j 정의 후 ( ctl_x, ctl_y, cbr_x, cbr_y ) 정의
정의된 좌표는 아래처럼 관계를 가짐

n은 홀수이며, central region의 크기를 결정함
3.3 Enriching Center and Corner Information
Center pooling : 기하학적인 중심은 인식 가능한 시각적 패턴을 전달하지 못하기에 이를 해결하고자 도입함
Process :
1) backbone이 featuremap을 출력
2) center keypoint인지를 확인하려면 수평, 수직 방향으로 maximum value 가져와서 합하기
Cascade corner pooling : corner은 오브제의 바깥에 있기에 local appearance feature이 부족
Corner pooling의 방식 : 경계 방향으로 최대값을 찾아서 코너 결정
이는 edge에 민감해짐
Sol 1) boundary를 따라서 boundary maximum value를 찾기
2) boundary의 지점에서 bbox 내부를 따라서 internal maximum value를 찾기
3) 2개의 maximum value를 더하기
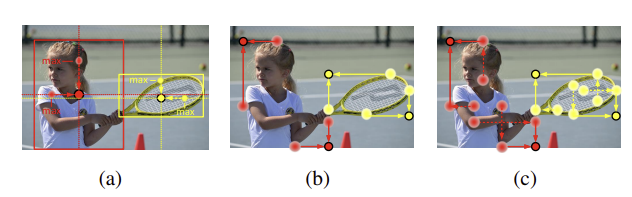
각 이미지는 (a) Center pooling, (b) Corner pooling only takes boundary direction
(c) Cascade pooling takes boundary directions and internal direction
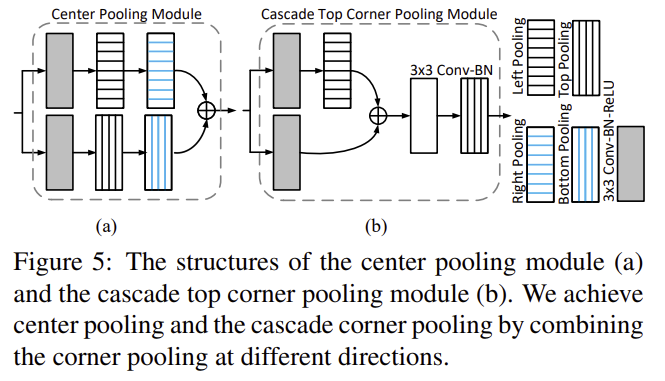
Fig5를 통해
(a) horizontal direction : only need to connect : right poloing, left pooling
(b) CornerNet과 다른 점 : top corner pooling 이전에 left corner pooling을 더한다
CenterNet's Loss

성능 평가

Incorrect Bounding Box Reduction
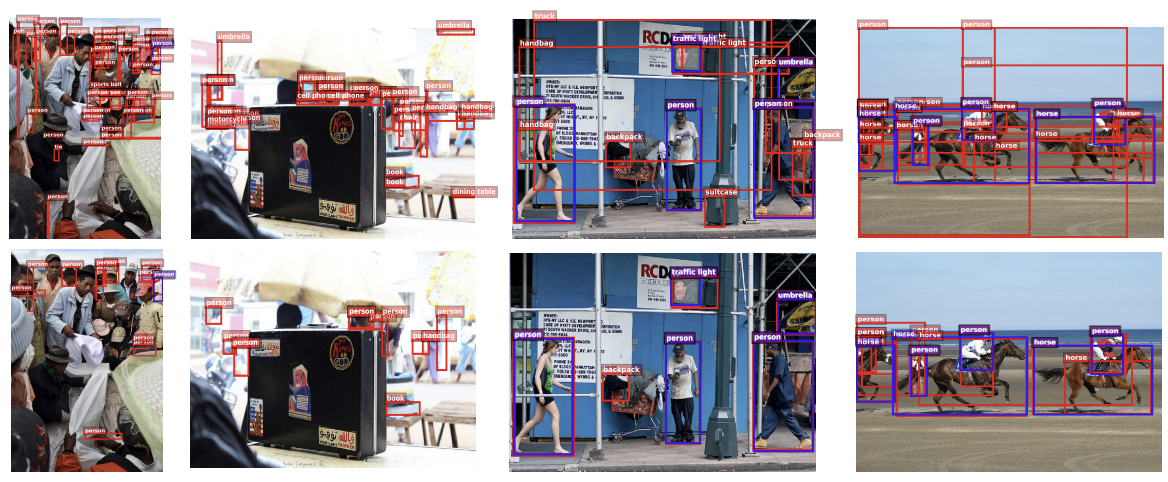

위와 아래 비교시 부정확한 bbox의 개수도 줄어들고 정확도도 늘어났음을 볼 수 있다.

center keypoint와 corner keypoint들이 위 아래로 비교시 오류가 줄어들었음으로 볼 수 있다.
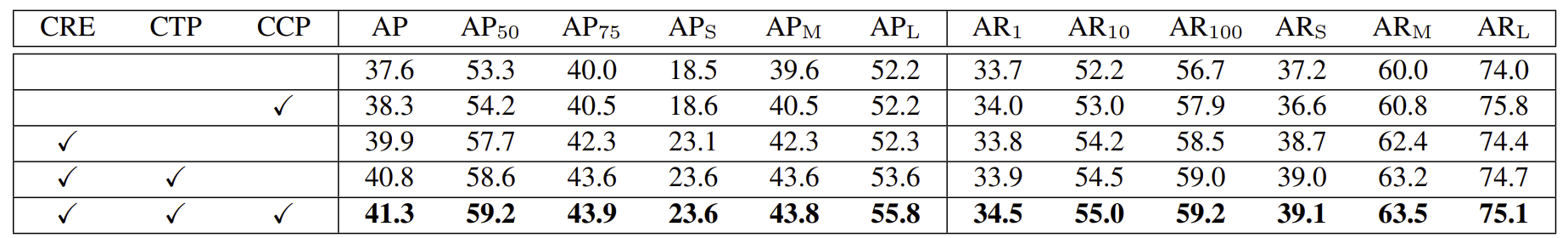
ablation study
CRE(central region exploration) : add center heatmap to the baseline and use a triplet of keypoints to detect bounding boxes
CTP(center pooling)
CCP(cascade corner pooling)

Error Analysis
Analyze the importance of center keypoints
마치며
cornernet과 centernet은 one-stage approach를 기반으로 문제를 해결하려고 했다.
Cornernet은 기존의 anchor box의 문제를 pair of keypoint를 통해
CenterNet은 오브제의 내부 정보의 확인을 위해 triplet을 이용해서 해결하고자 했었다.


