[2025-2] 박승원 - Learning representations by back-propagating errors
논문 링크: https://www.cs.utoronto.ca/~hinton/absps/naturebp.pdf
논문의 의의: 본 논문은 Back Propagation(오차역전파)를 인공신경망 학습에 체계적으로 적용하여, 다층 신경망 연구의 토대를 다진 연구.
Existing Works
- Neural Network를 만드려는 시도가 있었음.
- Input units과 output units이 직접적으로 연결되는 구조는 학습이 쉬웠으나, 흥미로운 결과가 도출되지는 않았음.
- Inputs과 outputs 사이에 hidden units이 존재하면 학습이 어려워지지만 더 흥미로운 결과를 도출함.
- 이 hidden units이 어떤 상황에, 얼마 만큼 활성화 될 지를 결정하는 것이 학습에 중요함.
Proposed methods
- 같은 layer 안에서는 unit끼리 서로 교류하지 않음.
- $x_j=\sum_iy_iw_{ji}$. 이전 layer의 output인 $y_i$에 가중치 $w_{ji}$를 곱함.
- $y_j=\frac{1}{1+e^{-x_j}}$. 이후 활성화 함수(주어진 식에서는 sigmoid 함수)를 사용하여 Non-linearity를 더해줌.
- 꼭 위의 식만 사용해야 하는 것은 아니며, 미분 가능한 함수라면 모두 사용 가능함.
- 위 식으로 계산된 결과를 ground truth 값과 비교하여 Mean Squared Error(MSE)를 loss로 사용.
- $E=\frac{1}{2}\sum_c\sum_j(y_{j,c}-d_{j,c})^2$
- Loss인 E를 gradient descent를 사용하여 최소화시킴.
- E를 minimize 시키면서 partial derivative를 활용하여 back propagation을 하여 각 가중치를 재조정.
- 특히, Chain rule이 이 과정에서 유용하게 사용됨.

결론적으로 Neural network의 depth를 늘릴 수 있게 되는 계기가 되었음.
* 외부 자료
위 논문을 통해서 Back propagation이 본격적으로 인공신경망 연구에 도입되고, hidden layer를 활용하여 시계열 데이터를 다루는 RNN이 등장하게 됨.
Recurrent Neural Network(RNN)
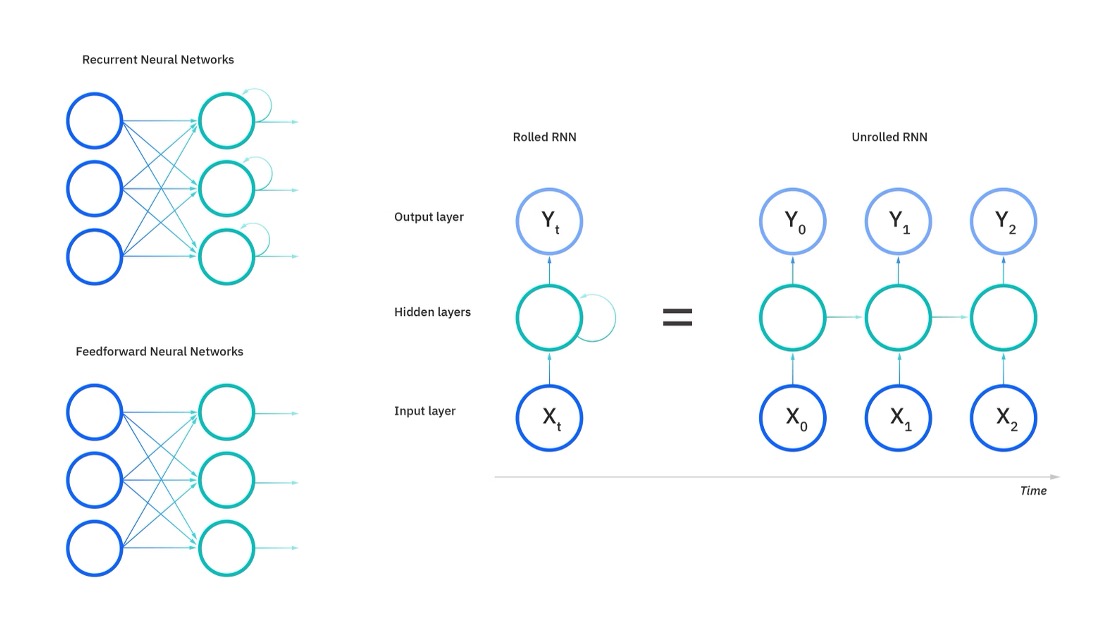
Properties of RNN
- Memory(이전 step의 hidden state)를 다음 state 계산의 input으로 받아 다음 hidden state와 output을 생성함.(이전 단계의 상태가 현재 상태에 영향을 주고, 현재 상태가 미래 상태에 영향을 주는 loop 형태라서 recurrent)
- hidden layer의 가중치가 모두 서로 같음.
- Back propagation을 layer 축이 아닌 시간 축으로 확장한 Back-propagation through time(BPTT) 사용.
Limitations
- Vanishing gradients - 시간이 많이 흐를수록 초기에 나온 정보를 잊어버림.(loss로부터 나오는 정보 흐름이 초기로 전달될 때 계속 감소되기 때문)
Types of RNN architectures
- Long Short-Term Memory(LSTM, ) -> Cell state를 활용하여 Long term dependency를 관리
- Gated Recurrent Units(GRU) -> 외부적인 Cell state를 사용하진 않지만 hidden state 업데이트시 필터링을 수행.
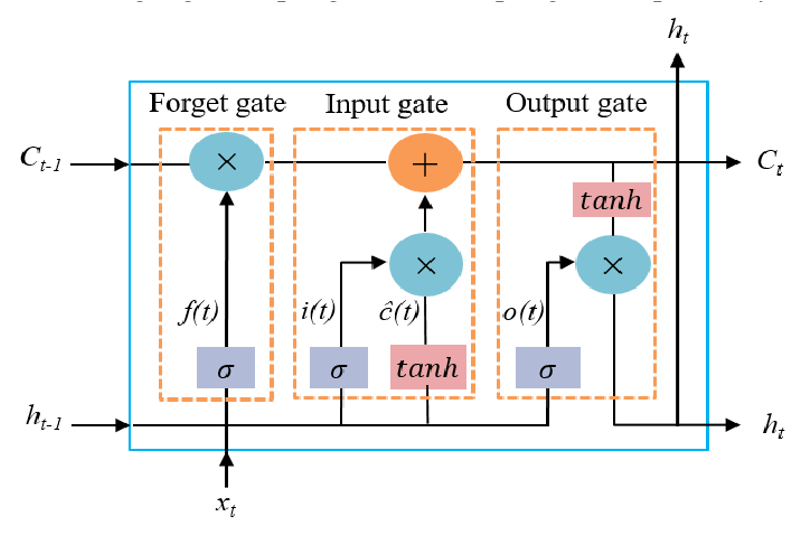
C_t: Cell state. Keep long term dependency infos
f(t): Forget gate. Decides what to forget from the cell state
i(t): Input gate. Decides what to update to the cell state
o(t): Output gate. Decides what to output as a hidden state
LSTM was proposed by Hochreiter & Schmidhuber, 1997
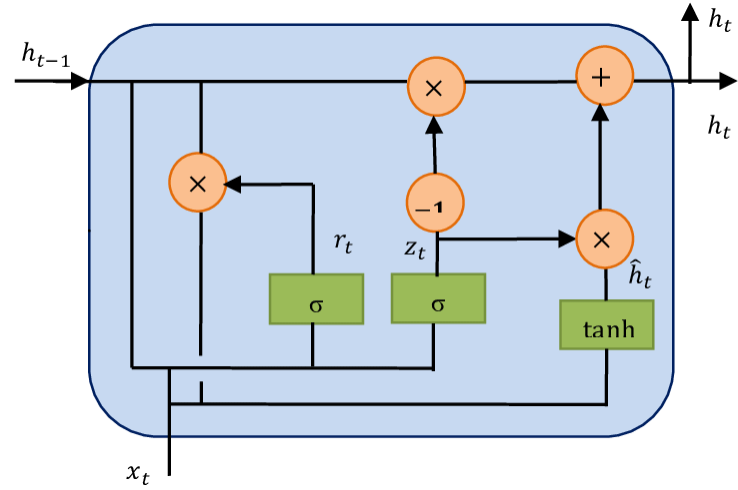
· No external cell state
· r_t: Reset gate. Decides how much to reset previous hidden state
· z_t: Update gate. LSTM’s forget + input gate
GRU was proposed by Cho et al., 2014